
Applying Multimedia Learning Theories to CPOE research based infographic and video screencast.
Introduction
To demonstrate the application of multimedia learning theories, I revamped an extraneous infographic and edited a stagnant screencast. The theories highlighted below are the Coherence Principle, the Spatial Contiguity Principle, the Multimedia Principle, the Segmenting Principle, the Active processing theory and the Cognitive Load Theory.

Original Research Snapshot Infographic pg. 1 
Original Research Snapshot Infographic pg. 2
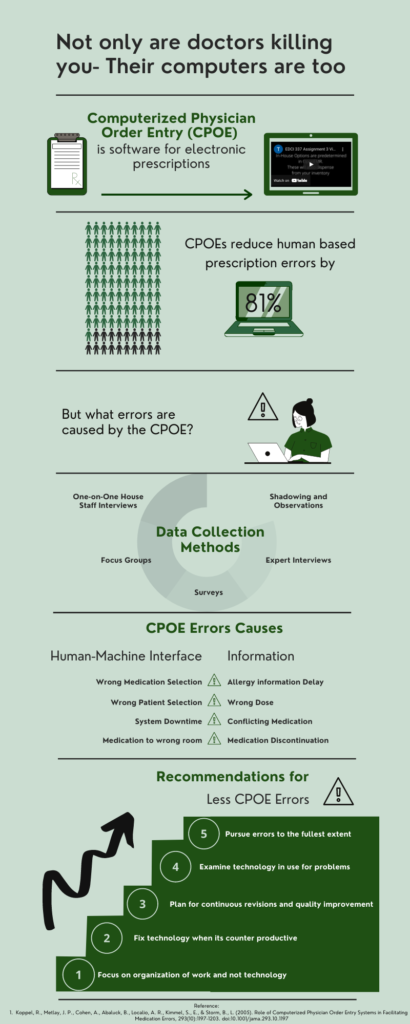
Layout and Design
The layout of the original infographic text was reduced to minimize extraneous information and therefore abide by the Coherence principle (McCue, 2021). The colour palette was limited to only 3 shades of green inorder to achieve a minimalistic and appealing appearance (Easelly, 2018). As seen in the images above, the updated infographic contains single sentence translations of entire paragraphs. Another element of design was inspired by the Spatial and Temporal Contiguity by strategic placement of images and text to convey a message (McCue, 2021). An example is the computer containing 81% and the graph for percentage to demonstrate error reduction. Infographics are efficiently simplistic as they relay information by use of complementary graphics. To apply the theory of limited capacity working memory I segmented the information with visual divides on the infographic (Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning, 2011). These visual divides can be identified by the horizontal lines where each segment only addresses a single topic.
Varied Information Media
The Multimedia Principle has been applied through the addition of video content to the edited video walkthrough that is embedded into the infographic. Additionally, the screencast follows the Dual-Coding theory as it caters to both sight and hearing senses to optimize working and long term memory. The original video screencast I created to demonstrate the abilities of a CPOE. To update and increase information retention, I applied the cognitive load and active processing theory through several video edits. The first video consisted of a single unedited shot with no pauses for learners to absorb the information while the second used transitions. These transitions followed the Segmenting Principle to allow people to learn each step at a time for a better learner-pace (Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning, 2011).
References:
Easelly. (2018, September 23). What Makes an Effective Infographic?https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rl9ZcfKt8sYCognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning. (2011, July 13). In ETEC510: Design Wiki. http://etec.ctlt.ubc.ca/510wiki/Cognitive_Theory_of_Multimedia_Learning
Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning. (2011, July 13). In ETEC510: Design Wiki. http://etec.ctlt.ubc.ca/510wiki/Cognitive_Theory_of_Multimedia_Learning
McCue, R. (2021, February 20). Introduction to Infographics with Canva & Related Multimedia Learning Principles [MP4]. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K1k3deWbw2c
Koppel, R., Metlay, J. P., Cohen, A., Abaluck, B., Localio, A. R., Kimmel, S., E., & Storm, B., L. (2005). Role of Computerized Physician Order Entry Systems in Facilitating Medication Errors, 293(10):1197-1203. doi:10.1001/jama.293.10.1197

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.